Key takeaways
The phrase number porting describes when a person or a business wants to move an existing phone number to another communications provider (CP) and keep the same phone number they had with the previous CP. This article will walk you through the steps to successfully move an active phone number to a different CP.
What is VoIP number porting?
When VoIP number porting occurs, business landlines are primarily ported to a VoIP service provider. Businesses that move a phone number from a traditional phone company to a VoIP service provider remove the burden of notifying clients about a new phone number. Businesses save money by eliminating the need to create new marketing and advertising material with updated contact information while allowing clients to contact them despite moving to a VoIP service provider. A mobile or VoIP phone number can also be ported to a VoIP service provider. However, the process is slightly different because landlines are assigned to a Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) phone and a specific location.
Why do you need to port a VoIP number?
A landline phone ported to a VoIP service provider allows your VoIP phone to use a VoIP port to connect to your computer and the internet. In addition to keeping your phone number, a business’s customers will have additional methods to communicate with the company. Additionally, after phone numbers are ported, the cost savings can be between 40% and 90%, as VoIP service providers are generally always cheaper than landline phone providers. Avoiding printing new marketing material and business cards also generates cost savings. Brand consistency is maintained in online listings, email signatures, and website contact information.
Porting to a VoIP number offers several additional features at minimal or no cost compared to adding advanced phone features to a landline phone. Advanced phone features come as standard options with a VoIP phone system that can be an additional cost if added to a landline phone. VoIP phones are more flexible and scalable than landline phones because VoIP phones are internet-connected, allowing the VoIP service to use hardware devices capable of making phone calls, too.
How to port to a VoIP number
Before porting a number to a VoIP service provider, there are specific steps to take. The first step is to confirm that your phone number is eligible to be ported to a VoIP provider because some providers do not support specific area codes or locations. Make sure your internet provider can support the selected VoIP provider’s bandwidth requirements and ensure your phone is compatible with the VoIP provider.
Verify that you are the only one using the phone number being ported. You can check by doing a reverse phone lookup with a service like Whitepages or Spokeo to confirm. After these pre-port requirements are verified, you can start making calls to your current provider and your selected VoIP provider to execute the following steps:
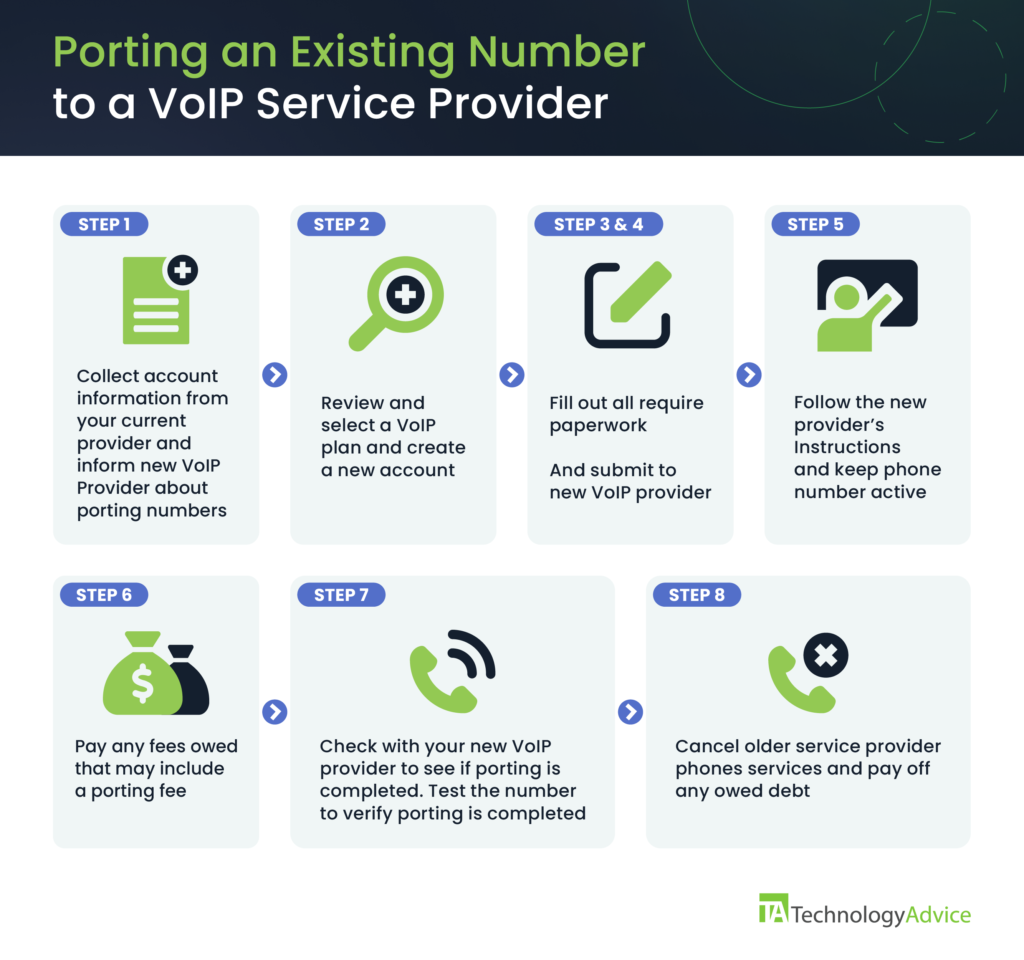
- Contact your current provider and let your new VoIP provider know you want to port a number.
- Review and select a VoIP plan and create an account with your VoIP provider.
- Fill out the necessary forms and provide the following information:
- Provide information about the number you are porting and include your account number and the name of the current provider
- Sign a Letter of Authorization (LOA) and share the PIN
- Ensure the person authorizing the port move is the same person signing the additional paperwork.
- Provide an accurate billing address, and PO Box addresses are not an option
- Keep your current landline phone service active until the porting process is complete, and in the meantime, you can use a temporary number to forward your calls until the porting is complete.
- Pay any fees, which may include a porting fee
- The porting process can take as long as ten business days, but each VoIP provider has different timelines for completion. Check with your selected provider for an estimated completion date.
- Close your old service provider account after confirming the number has successfully been ported to the VoIP provider. See Figure 1 to review the steps to port a number to a VoIP provider.
Is porting a landline or mobile phone different from a VoIP phone?
The porting process is the same across landline, mobile, and VoIP numbers, and the difference boils down to how many numbers are being ported. The most notable difference when porting VoIP, landline, or mobile numbers is the time it takes to complete the porting process. Mobile or cellular, VoIP, and landline phones have different timelines for completing a successful port, but companies like Verizon and AT&T have their porting process with established timelines.
Landline numbers use Local Number Portability (LNP) and can port numbers to VoIP providers the fastest. Mobile numbers use Mobile Number Portability (MNP), which takes 5-10 business days to port number(s). Porting VoIP numbers takes the longest due to making the number accessible across multiple devices, and the completion timeline is similar to mobile numbers.
For any business going through the porting process, you can use call forwarding through Interim Number Portability (INP) or get a temporary number from your new provider. One common delay, regardless of the type of number being ported, is incorrect or missing documentation. For any CP to meet their estimated completion timeline, submitting correctly filled-out documentation will help the provider meet their completion dates.
Requirements for VoIP porting
Specific requirements must be met before a number is ported to a new provider. The account must be in good standing with your current provider without a history of past-due bills. You must be with your current service provider for at least 60 days before you can cancel. As mentioned earlier, your phone must be currently active. You own the phone number exclusively and sign and provide a LOA with a recent phone bill that shows the number you are porting. Again, verify the selected VoIP provider covers the location you plan to work from with VoIP phones
Ensure your phone(s) is compatible with the selected VoIP provider and provide a list of phone numbers along with the porting out PIN information that authorizes the port transfer. Sometimes, the new VoIP provider will contact the current provider on your behalf and get the required information. The porting process can take from 5 days up to 6 weeks, depending on the number of phones and the complexity of the task.
Benefits and challenges of VoIP number porting
There are pros and cons when porting to a VoIP number. An advantage of porting to a VoIP provider is the portability, which keeps teams and customers connected regardless of location. VoIP phone systems are excellent for companies that want to excel at customer service due to the available communication options. Portability allows 24/7 access to files, features, and contacts as long as a good internet connection exists. VoIP phones provide excellent voice quality due to packet switching technology that minimizes jitters in voice quality, connectivity problems, and call drops. Other notable benefits are the following:
- Lower costs: Advanced features come as standard features with a VoIP phone, and it’s easier to upgrade or modify your existing contract to meet any new business needs.
- Integration: VoIP phone systems integrate easily with customer-focused business applications like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, text messaging software and email.
- Mobility: A working internet connection will allow an employee to make or receive a call anywhere in the world.
- Advanced phone features: Call management features such as voicemail, call forwarding, call routing, and call parking are advanced features that help businesses distribute calls to the appropriate person.
- Conference calling: Conference calls can be audio or video meetings with screen share functionality over the internet.
- Toll-free numbers: Business VoIP phone system can include toll-free numbers, which is ideal for a startup or small business.
- Flexibility and scalability: VoIP phone systems are flexible and capable of adapting to change quickly, scaling up to meet increasing workloads and scaling down when required.
- Advanced analytics: VoIP systems allow for real-time monitoring and conversation intelligence, allowing management to gain insight into customers’ expectations and sentiments.
- Unified Communications (UCaaS): It helps improve user experience by providing users with different communication methods such as desktop, laptop, tablet or smartphone to communicate seamlessly.
- Toll-free numbers: Some business VoIP systems provide toll-free numbers, while some providers offer free VoIP phone services.
Challenges of VoIP number porting
On the flip side of the benefits of VoIP number porting, there can be some challenges a business may need to overcome. The most concerning issue is that VoIP services may not be compatible with emergency services. Some VoIP providers may not have an interconnection agreement with your current phone service provider. Other known challenges that may arise are:
- Coverage: A specific VoIP provider may not provide coverage in your area.
- Bandwidth limitations: The VoIP phone service will most likely run on your business network, and the additional bandwidth requirement for VoIP services may impact existing IT resources on the business network, which can degrade the network for all IT services.
- Phone number status: A projected number identified as portable may be inactive, which means it cannot be ported.
- Geographic restrictions: A possibility exists that some phone numbers may be restricted from being ported due to service areas or rate centers due to calling boundaries for specific phone numbers.
- Security: VoIP phone systems may be vulnerable to fraud that allows scammers to hijack lines to make calls that the business must pay for.
- Documentation errors: Incomplete or errors in the required documentation can cause unexpected delays between service providers.
- Network architecture compatibility: A network upgrade may be needed to accommodate the VoIP provider services.
Best practices for VoIP number porting
Change will always occur as IT technology advances to improve business operations, but a backup plan can minimize downtime if an unplanned incident occurs. Best practices are essential if something unanticipated happens, and it begins with a backup plan. Communicating early and regularly with your current and new provider is a crucial best practice. Other best practices are:
- Understand the terms and conditions: Ask as many questions as necessary until you clearly understand the service agreement, pricing, and any potential future upgrades.
- Configure your VoIP account: As soon as your VoIP account is created, log in and set up your account.
- Coordinate porting dates: Coordinate proposed porting dates that minimize disrupting your business operations.
- Comply with porting requirements: Verify all porting requirements are met, including active number, no pending orders, and no outstanding balances.
- Eligible phones: Not all phones are eligible for porting as some phones may have restrictions such as prepaid phone numbers.
Guide to choosing a new VoIP provider
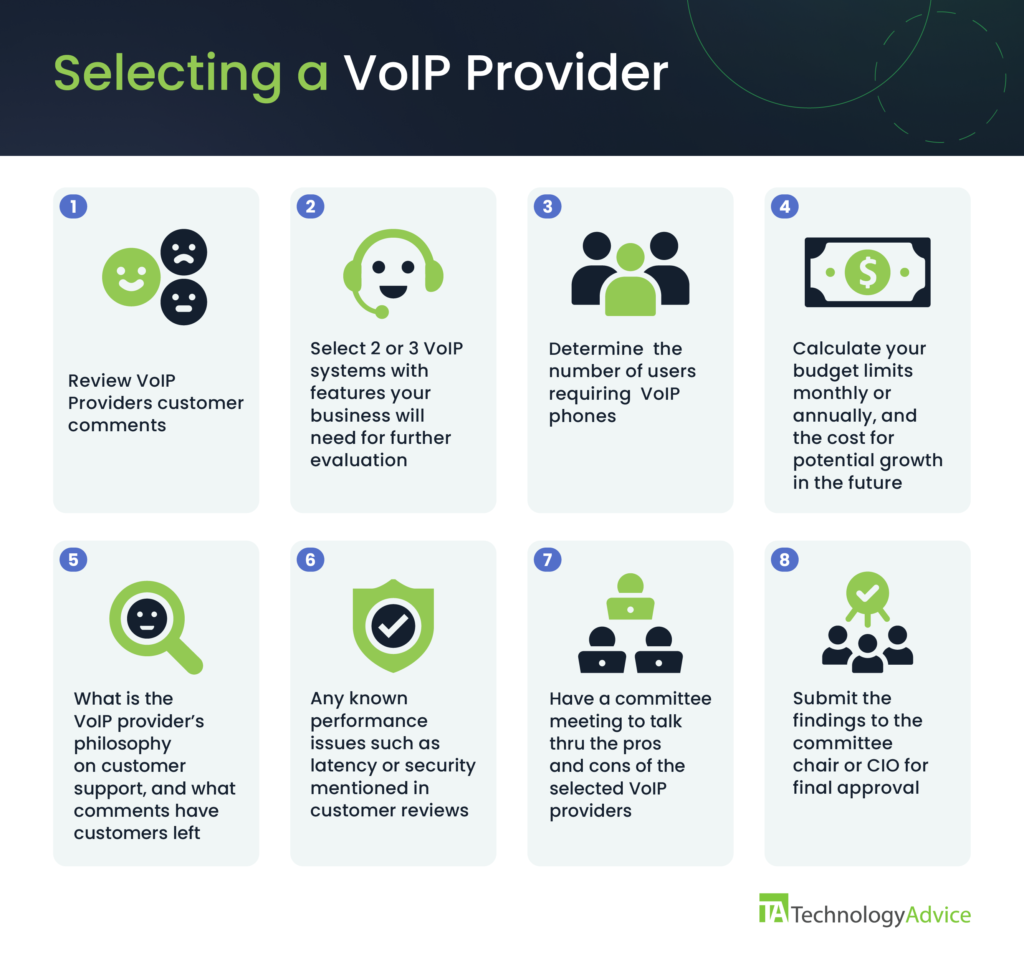
A business looking for a VoIP provider can start by forming a committee from various departments to garner input from every department. Companies must decide on the type of VoIP system needed and the primary features the VoIP system will need to conduct everyday business. What will also influence your business decision is whether you are getting a new VoIP system, replacing an old system, or expanding an existing VoIP system. If VoIP technology is new to an organization, contracted assistance may be required.
The selection process can begin by reviewing VoIP’s customer comments on various websites.
- Reviewing different website reviews will provide a holistic view of their customer base to assess a VoIP provider’s performance.
- Select a VoIP system and must-have features:
- Hosted PBX – hosted on a business on-site location in a data center
- Cloud-based – uses cloud-based technology that allows users to execute mobile VoIP functionality globally with a good internet connection
- Unified Communication (UC) – is a complete business communication suite designed for teams working remotely routinely. Unified Communication includes video conferencing, instant messaging, screen sharing, call forwarding, and more advanced features
- Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) – is more robust than UC, featuring high-tech integrations and advanced functionality
- What communications features are needed
- How many users need VoIP phones
- Determine the monthly or annual budget requirement
- What are your customer support requirements
- Any VoIP provider issues, such as security or latency that are notable
- Compare your top VoIP providers and what’s uniquely offered, and compare what features are included as standard options
- Present the findings to the CIO or committee chair for final approval. See Figure 2.