Key takeaways
Data governance is a foundational component of any successful business. It uses information technology (IT) resources to execute internal and external business processes. The IT resources used to perform daily business operations will be useless if the processed data is inaccurate or corrupt. Data governance aims to manage the validity and accuracy of business data from its inception to obsolescence, including the proper disposal of outdated data.
What is data governance?
Data governance consists of a set of processes, procedures, and rules that dictate the proper use of business data throughout its life cycle. The data governance framework ensures business data is accurate, available, usable, secure, and protected for data analysis processes and from unauthorized users gaining access.
Data governance allows authorized users to locate, prepare, use, and share data with other authorized users. It helps businesses safeguard their data, grant access to authorized users, and distribute it as needed.
Read more: Data Governance Can Ease PII Regulation Compliance
Why is data governance important?
Data governance is essential because it outlines the proper actions users must take when using data. It provides approved and authorized processes for users to follow and specifies the authorized technology used throughout the data’s life cycle to ensure it stays within expected parameters. Data governance helps businesses manage and govern proprietary data responsibly and effectively by using approved processes and technology employees use to accomplish daily tasks.
Data governance ensures businesses meet any regulatory compliance for legal obligations. It also improves data quality and efficiency by removing errors or duplicate data from datasets. The data governance framework allows for better decision-making while ensuring the data is secure and protected by preventing data leaks or exposure through an IT vulnerability. Effective data governance ensures consistency and trustworthiness throughout any data’s life cycle.
Read more: What Is Data Mining?
Data governance vs. data management: What’s the difference?
Data governance and data management are integral parts of the data governance framework. Data governance operates strategically by establishing policies, procedures, and strategies for managing data. In contrast, data management is more tactical in how data should be appropriately handled, processed, and used.
Data governance focuses on establishing policies, procedures, and strategies for managing data that involve availability, usability, security, and integrity. Additionally, governance focuses on the people using the data, the technology that manipulates the data, the processes aligned to data roles, and how well the processes support the business’s data strategy.
Expert Tip
Data management is the execution piece of the framework that implements the outlined initiatives in the data governance strategy by using the established methods, policies, and procedures for data management.
Data management is the collection, storage, protection, and utilization of data that can involve data entry, database design, information retrieval, and data warehousing while using the best security practices. Data management adheres to established data governance parameters while meeting short- and long-term goals that ultimately meet the long-term objectives of data governance.
Data governance establishes the rules, policies, and procedures, including the overall objectives, and data management uses the established specifications from data governance to meet short- and long-term goals and objectives.
Read more: Data Cleaning: Definition, Techniques & Best Practices
Data governance framework
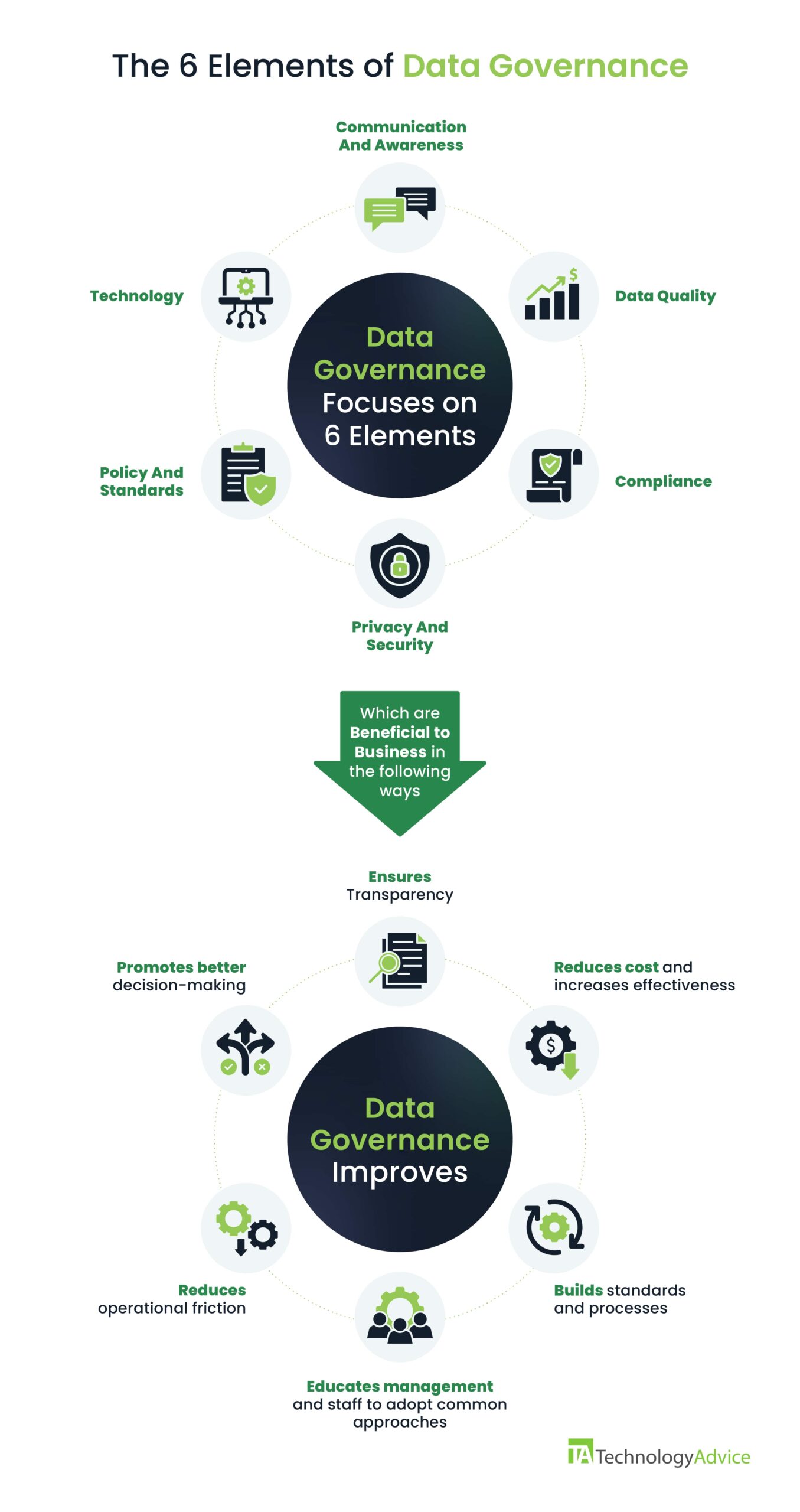
The pillars of the data governance framework are data quality, privacy, compliance, and security. The data governance framework is paramount throughout the data life cycle, as it dictates specific actions from creation to disposal of any data type, including metadata.
The data governance framework is a set of rules, processes, and responsibilities that mandates how businesses manage their data, including accountability to people, processes, and technology.
The purpose of the data governance guide is to ensure data integrity is maintained, allow employees to use data effectively, and protect it from security risks. The data governance framework helps businesses maintain compliance with policies and regulations, promote authorized data sharing, and quantify results.
Benefits and challenges of data governance
Quality decision-making begins with data that truthfully represents an accurate picture of a business’s profits, efficient processes, available product resources, and the ability to promote growth while allowing employees to continue excelling. The data governance guide provides the following benefits:
- Enforce and monitor data policies: Ensures policies, rules, and definitions apply to all business data, including security, accuracy, and quality.
- Increased operational efficiency: Identifies areas of improvement, allowing managers to allocate resources better and adjust workflows as required.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensures businesses comply with regulatory requirements like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
- Enhanced transparency: Provides a shared understanding across the entire organization.
- Reduced costs: Improves data quality to eliminate or minimize mismanaged data and repeated data mining or data cleansing efforts.
- Improved data management: Establishes structure, policies, and rules for properly managing data throughout its lifecycle.
- Improved data-driven decisions: Ensures data is accurate and trustworthy for better decision-making.
- Enhanced collaboration between teams: Clearly defined data roles and a unified view of data help eliminate silos and encourage better communication.
Challenges of data governance
A data governance program not supported by senior leadership is a significant threat that can eventually lead to failure. A robust data governance program must be supported by all levels of management, including a repeatable data governance training program that holds all employees accountable.
Other challenges include:
- Fragmentation and siloed data: Isolated data must be identified to validate its usefulness.
- Data literacy and culture: All employees need to understand the importance of data to minimize resistance and misuse.
- Limited resources: Budget constraints can hinder acquiring necessary training, tools, and expertise.
- Resistance to change: Some employees may resist adopting a data governance program.
- Poor data quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency is paramount.
- Data security: Understanding data states helps in applying the best security tools.
- Data accountability: Employees must understand proper data usage; data stewardship teams can help.
- Data integration: Maintaining data trustworthiness after integration is challenging.
- Data compliance: Staying aware of changing compliance regulations is essential.
Read more: Common Data Quality Issues & How to Solve Them
Data governance best practices
Data governance best practices begin with upper management fully supporting data governance and recognizing that best practices must be implemented to maintain accurate and trustworthy data.
- Managing data access: Only authorized and trained users should access data. Data owners must ensure data remains trustworthy.
- Establishing roles and responsibilities: Data stewards and owners maintain consistent data management standards. Administrators oversee data integrity and analytics.
- Develop and enforce data quality standards: Regular checks ensure data maintains established quality standards.
- Stakeholder involvement: Involving stakeholders from different departments ensures organizational alignment.
- Implement data security: Updated security methods like multi-factor authentication prevent unauthorized access.
- Automation: Tools that perform data quality assessments without constant human intervention are essential.
- Adopt a continuous improvement mentality: Continuously challenge the data governance program to adapt to changes.
- Document data: Keep all data documentation, such as metadata and data dictionaries, updated.
Read more: Data Analysis Methods.
Data governance products and solutions
Data governance tools help staff connect data through people, processes, and technology to achieve better business results.
Alation
Alation is a data intelligence platform that helps businesses understand what data exists and how it’s used. It assists in managing risks, compliance, and data privacy issues and aids in cloud migration by identifying dependencies.
SAP Master Data Governance (SAP MDG)
SAP MDG allows businesses to define, enforce, monitor, and improve master data across multiple IT domains. It enhances data quality by adding views of master data associated with relevant information from different applications, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Collibra
Collibra is a data governance platform that protects and manages data while maximizing its value. It uses a centralized platform for defining, implementing, and tracking data policies and standards, enhancing decision-making and ensuring regulatory compliance.





