Key takeaways
Disclaimer: TechnologyAdvice is not a tax or legal service/agency. The portions of this article about federal, state, and local employee and employer tax withholdings are for informational purposes only and are not intended as legal advice. Please consult your accountant, tax expert, or labor law attorney for specific situations.
Free payroll spreadsheet template
DIY payroll can be scary, but our payroll spreadsheet template is a great starting point. Use it to calculate paychecks for your employees, including tax liabilities at the federal and state levels.
Download our payroll template for free:
How to do your own payroll
Payroll is a complex and time-consuming process. Your employees depend on payroll for their livelihoods, so accuracy is vital. Besides employee frustration and anger, payroll mistakes can also lead to hefty fines, audits, and even jail time, depending on the error and its frequency and severity.
That said, running payroll yourself is possible. And if you’re a new startup or small business owner with 10 or fewer employees, it’s often more practical to process payroll manually before investing in a service or software solution.
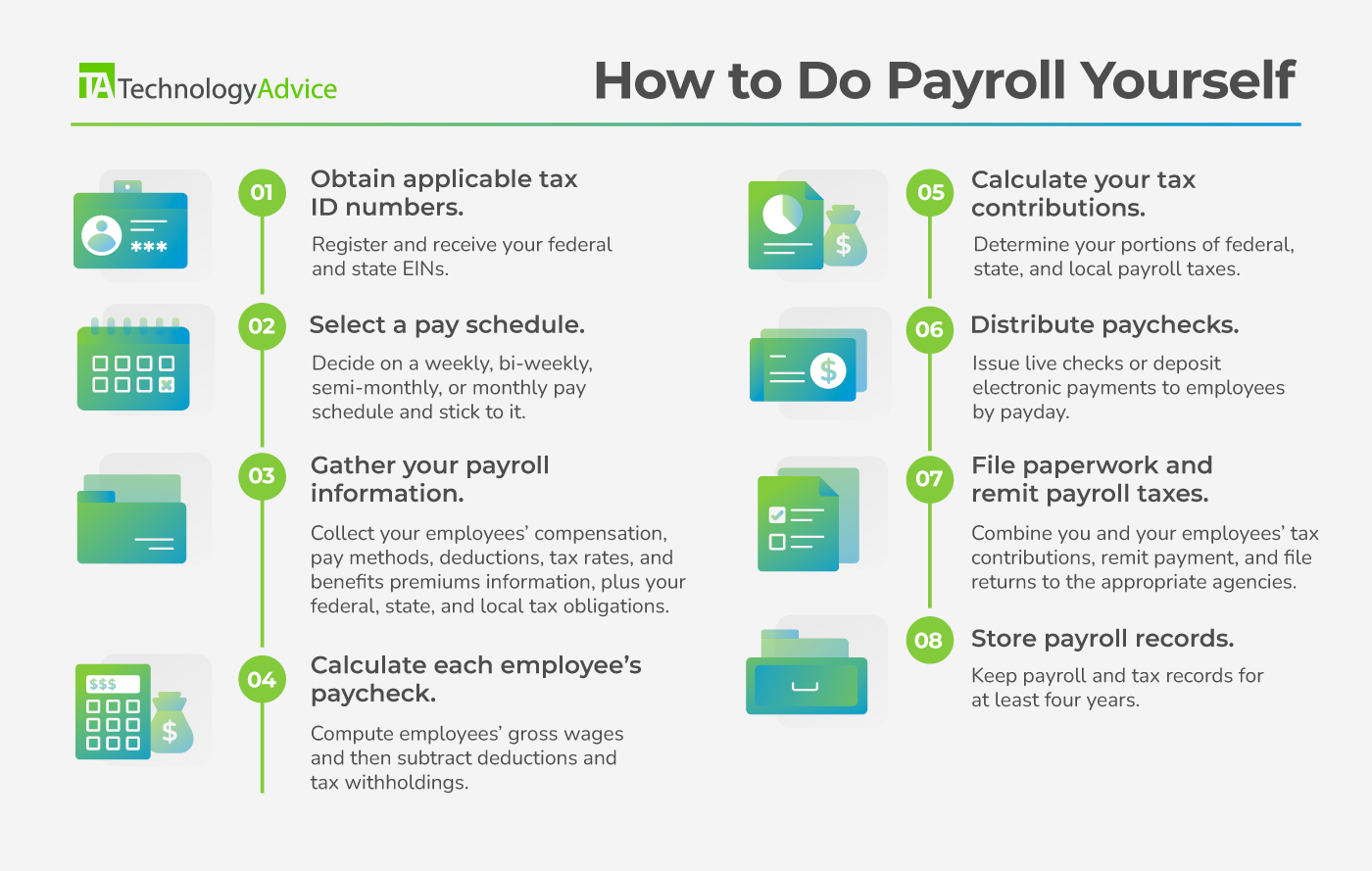
Here’s a summary of the steps involved:
If doing payroll yourself looks daunting, you have other options. Check out our Best Free Payroll Software and Payroll Software Guide for free and low-cost solutions that can handle the majority of this process for you.
Before you start
This guide will help you complete payroll for workers who are classified as employees, not contractors. There are three things to do before processing payroll for the first time:
- Familiarize yourself with the state and local labor and tax laws of your employees. This how-to goes into depth about calculating federal payroll taxes but only provides cursory guidance on state and local laws. Understanding the payroll laws where your employees live and work will reduce the likelihood of inaccurate deductions and tax contributions from you and the employee.
- Understand common payroll terms. Jump to our payroll glossary and learn about this guide’s different terms.
- Decide on your do-it-yourself (DIY) method. You’ll need a paper payroll record book with a pen and calculator or a basic computer spreadsheet program to calculate and track your payroll expenses. Pro tip: Download our payroll template to get started.
Although paying contractors is similar to paying business vendors, they’re not identical processes. If you only need contractor payroll, there are several software platforms that can simplify the process. Most vendors typically offer contractor-only subscription plans at lower costs than their full-service payroll subscriptions.
Check out Top Contractor Payroll Solutions to learn more.
1. Obtain applicable tax ID numbers
Before digging into the logistics of payroll, you must first apply for a federal Employer Identification Number (EIN) with the IRS. Without an EIN, you won’t be able to open a business bank account, hire employees, or file federal, state, and local taxes. You might also need to obtain separate tax IDs for each state, county, and/or city where your business operates depending on your tax obligations.
After you receive your EINs, register with the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS). This free system by the Department of the Treasury lets you electronically pay your federal payroll taxes in one place. All employers must use this system for remitting tax payments, so it’s a good idea to have your account ready before your first payday.
Several payroll providers can help you obtain your EINs in multiple states. Gusto, for example, offers state tax registration services alongside its payroll platform. It will handle all the paperwork and keep you updated on the progress.
2. Select a pay schedule
The four most common pay schedules are:
- Weekly (52 pay periods per year).
- Bi-weekly (26 pay periods per year).
- Semi-monthly (24 pay periods per year).
- Monthly (12 pay periods per year).
The best schedule for your business depends on your cash flow and the types of workers you have.
For example, let’s say you offer a monthly subscription service and bill customers on the 15th or the last day of the month, depending on when they signed up. A semi-monthly payroll schedule would align with your cash influx and ensure you have enough money to pay your labor costs on time.
In contrast, a weekly schedule may be easier if you have many non-exempt hourly employees, as it is much simpler to calculate overtime payments. Factoring in the employee experience is also important, as workers in some industries, like construction, may expect their paychecks at a particular frequency.
The FLSA requires employers to pay their workers at least monthly. However, most states have pay schedule laws regulating payday frequency and how long you can wait to pay employees following the end of a pay period.
To see the pay frequency laws that apply to you, check out Wage and Hour Division’s (WHD) State Payday Requirements.
3. Gather your payroll information
At the end of your pay period, you’ll need the following information to process payroll:
4. Calculate each employee’s paycheck
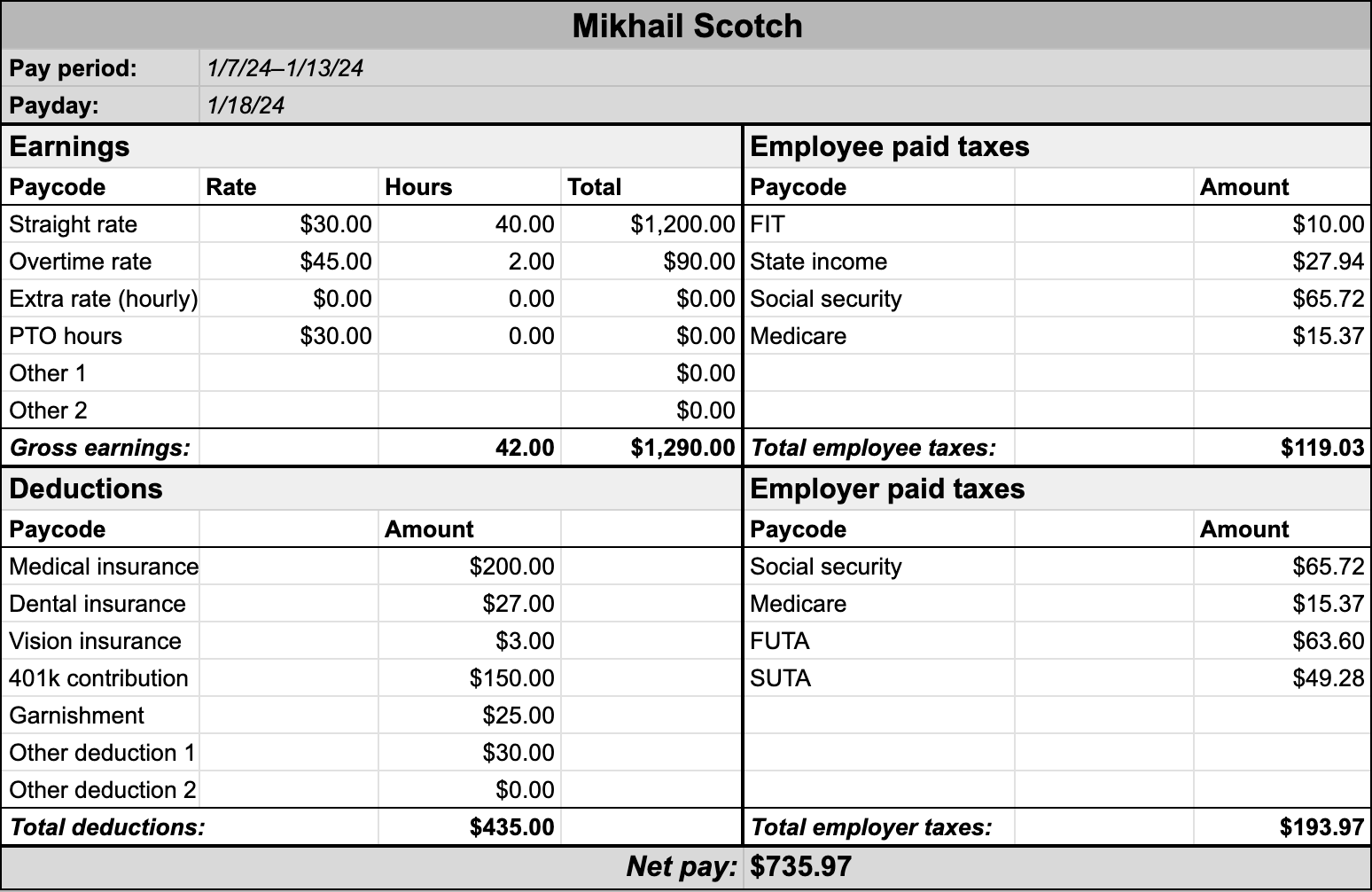
Let’s use an example to calculate an employee’s paycheck step-by-step. Here’s an employee record for Mikhail Scotch, the regional manager at a paper company called Blunder Bifflin:
Name: Mikhail Scotch
Title: Regional Manager
Branch: Scranton, PA
Straight-time rate: $30 per hour
Overtime rate: $45 per hour
Pay schedule: Weekly
Medical: $200 per paycheck
Dental: $27 per paycheck
Vision: $3 per paycheck
Pet: $30 per paycheck
401(k) contribution: $150 per paycheck
Garnishments: $25 per paycheck
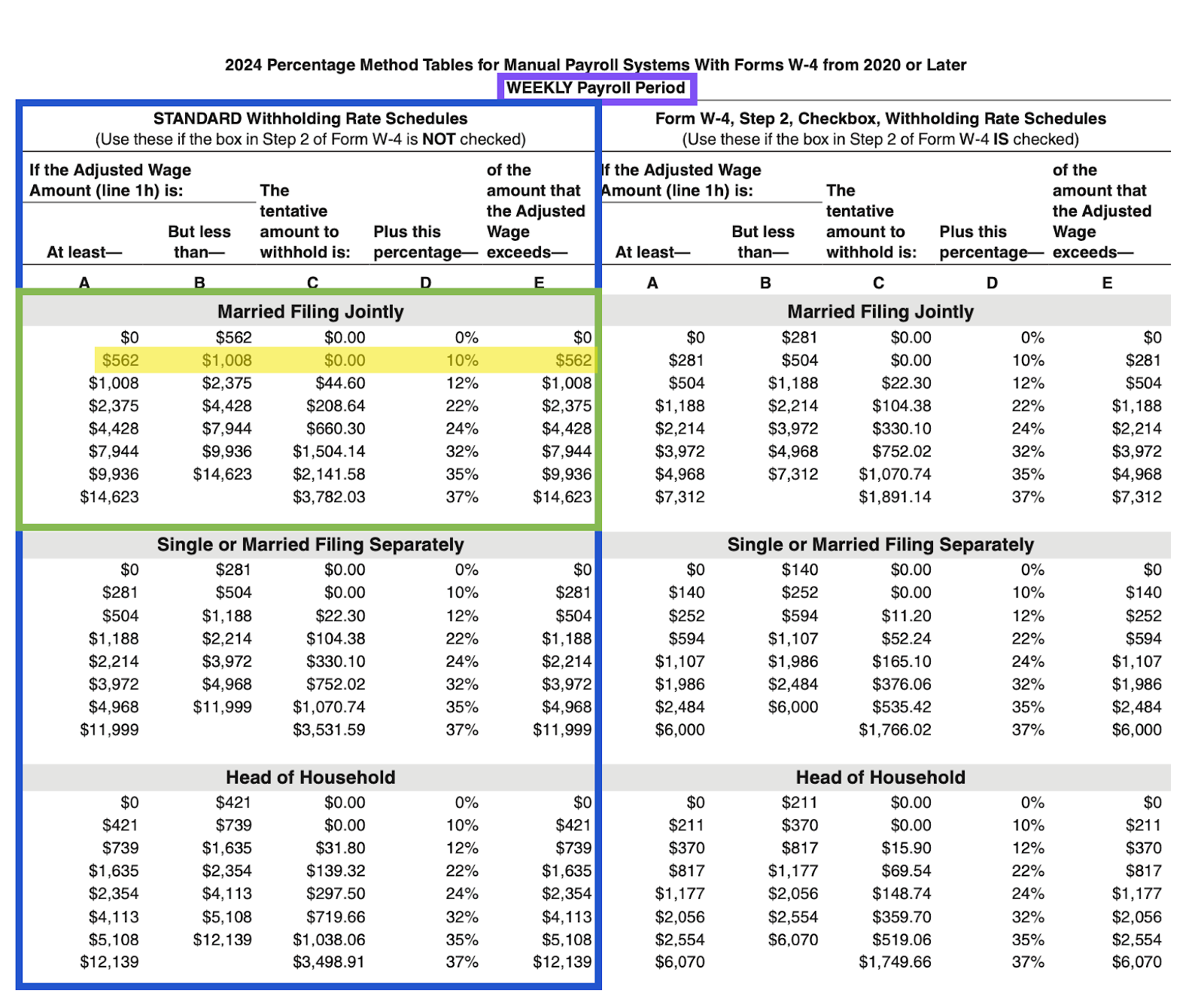
Filing status: Married, filing jointly
Dependents: One
Expected interest payments for 2024: $1,500
Additional withholding amount: $10
Pennsylvania state income tax rate: 3.07%
To calculate Mikhail’s paycheck amount by hand, we need to determine his gross pay, deductions, taxes, and net pay in order. This is where it can get tricky — take your time and double-check each detail to avoid costly mistakes.
5. Calculate your tax contributions
As an employer, you are responsible for withholding and remitting all employee-specific payroll taxes on their behalf. However, you must also calculate and remit employer-specific federal, state, and local payroll taxes.
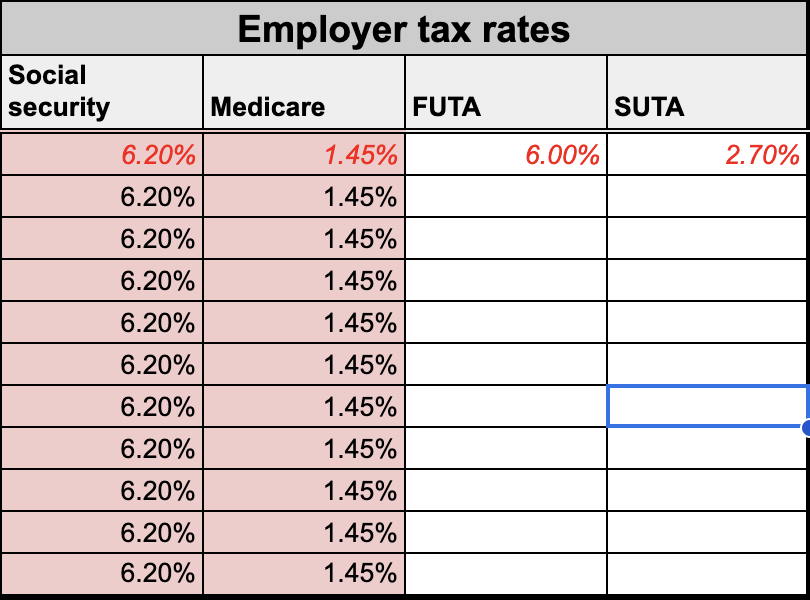
Federally, you must pay FUTA plus match your employees’ FICA contributions. As of 2024, the FUTA tax rate is 6% with a $7,000 taxable wage base, but you can get a 5.4% tax credit if you pay your state unemployment insurance (SUTA) on time. This means you only pay 0.06%.
FICA is easy to determine since your Social Security (6.2%) and Medicare (1.45%) tax rates match what your employee pays. Like your employee, you also stop paying the Social Security portion of FICA once they hit the taxable wage base for the year.
You’re also responsible for paying SUTA. You’ll receive your SUTA rates from your respective state agencies. Most states base their rates on your unemployment history, so the fewer employees you have claiming unemployment benefits historically, the lower your unemployment rate. Some states also take your industry into account.
For other state or local taxes, research the employer tax requirements in each state you have employees and remit these amounts accordingly.
Continuing the Mikhail Scotch example above, assume we’re in a low-risk industry — paper sales. Our FUTA rate is 6% and our SUTA rate for Pennsylvania is 3.82%. Let’s figure out our portion of taxes for Mikhail below.
| 1. Social Security tax ($1,060 X 0.062) | $65.72 |
| 2. Medicare tax ($1,060 X 0.0145) | $15.37 |
| 3. FUTA tax ($1,060 X 0.06) | $63.60 |
| 4. SUTA tax ($1,290 X 0.0382) | $49.28* |
| Total employer taxes | $193.97 |
*Double-check what the employee’s state considers taxable income for SUTA purposes. Generally, it is the same as gross pay, without pre-tax deductions.
6. Distribute paychecks
Once you’ve processed payroll, you must distribute everyone’s paychecks via the payment method they chose during onboarding. Remember to send positive pay information to your financial institution if you issue live checks.
Employees should also receive their pay by their scheduled payday. In some states, like California, you may incur waiting time penalties for every day late. You must also present a paystub to the employee as proof of payment, even if they receive it electronically.
Although payroll processing times differ for each company, direct deposits generally take at least one to three days to reach employee bank accounts. While you can print and hand-deliver checks to your on-site staff, you must ensure you mail checks early enough to reach your off-site employees by payday.
Learn more about how long it takes to process payroll from start to finish:
Payroll software speeds up payment processing
Of course, payroll software can simplify paycheck calculations and tax filings. However, what you may not realize is the time you save using payroll software to print checks and send direct deposits to employees within the platform. Several payroll vendors even offer their own paycheck signing and delivery services.
Moreover, these solutions automatically produce paystubs that employees can access 24/7 through online portals. RUN Powered by ADP, for example, offers check delivery services, so you don’t have to visit the post office to send paychecks for each payroll. Its online portals mean employees can access their pay whenever it’s convenient for them.
7. File paperwork and remit payroll taxes
Keep tabs on how much you owe in payroll taxes for each employee. Depending on the tax, you must remit these payments to various agencies on different schedules. Usually, the schedule for filing payroll tax returns differs from when you remit payments. Check with your employee’s state treasury department for information on these schedules.
As for depositing federal payroll taxes, FIT and FICA taxes are due to the IRS semi-weekly or monthly, depending on your tax liability. FUTA deposits also depend on your tax liability but generally occur only once a quarter or longer. You must submit all payments through the Department of the Treasury’s EFTPS.
In addition, you must submit tax returns at the appropriate time. Form 940 details your FUTA payments and is due annually on January 31 for the previous year’s data. Meanwhile, Form 941 shows your FIT and FICA payments. You’ll file these quarterly by the last day of the month following the end of each quarter.
Check out the IRS’ employment tax due dates page for more information on tax filing and deposit schedules. You may also want to speak with an accountant or tax advisor to ensure you meet all deposit and filing schedules for federal, state, and local payroll taxes.
8. Store payroll records
The FLSA requires you to keep employee wage information for at least three years, while the IRS requires you to keep income tax records for at least four. Other payroll records have longer or shorter storage requirements, depending on state and local jurisdictions.
You’ll also need to keep payroll records for the year to send W-3 forms to the IRS and Social Security Administration (SSA) and W-2 and 1099-NEC forms to your workers. W-3 forms summarize the information on W-2 forms and are due to the IRS and the SSA on January 31. Similarly, W-2s and 1099-NECs are due to your employees and contractors on January 31.
Thorough payroll recordkeeping simplifies year-end payroll paperwork and minimizes compliance issues in case the IRS audits you. In fact, periodic payroll audits are a great way to improve your payroll process efficiency while proactively addressing issues before they become major problems.
Advantages of doing your own payroll
In some cases, calculating your own payroll is the most affordable and practical option.
Cost
Processing your own payroll means you don’t have to budget for software or third-party services. Although it requires more time and energy, running payroll on your own allows you to prioritize other operating expenses that might be more important.
Practicality
If you know the basic calculations, manual payroll processing means you don’t need to spend time learning how to use new software. Similarly, outsourcing your payroll or leveraging advanced technology may be impractical if you only need to pay a handful of employees.
Disadvantages of doing your own payroll
Running payroll by yourself can be time-consuming, prone to human error, and legally risky.
Time constraints
Running payroll by hand takes a lot of time, especially if you have more than one or two employees. Besides how long it takes to process paychecks, you also spend valuable time researching payroll laws and complying with tax deposit and filing schedules.
Payroll software simplifies the whole process and allows you to spend your time on more valuable tasks. Some solutions can even run payroll and issue direct deposits automatically, so you don’t have to worry about remembering your payroll schedule.
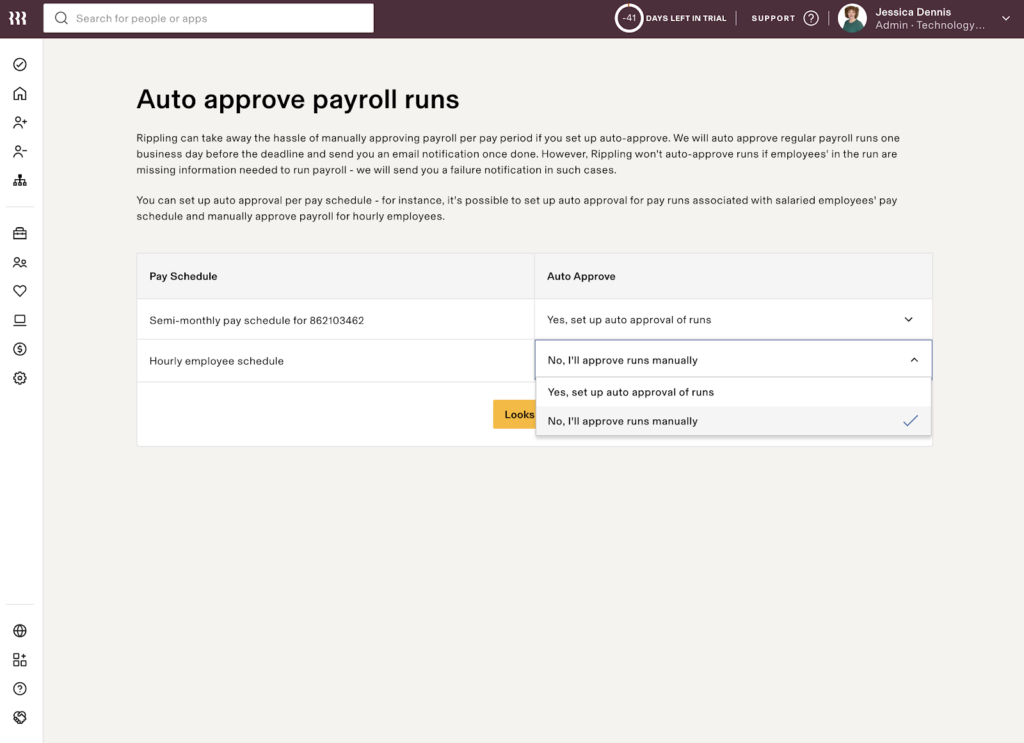
Rippling, for example, includes an auto-approve payroll feature that processes payroll automatically as long as you’re not missing any important information.
Human error
Processing payroll on your own also significantly increases the chances of errors compared to using software. You might enter the data incorrectly or make a mistake while calculating wage garnishments by hand.
You must also account for any updates each pay period, such as new state or federal income tax rates or increased employee withholding allowances. Such frequent changes also increase your chances of making mistakes.
However, most payroll software includes code to minimize errors. Paycor, for example, has in-app warnings for shortfalls, missing employee information, and duplicate Social Security numbers to prevent mistakes before you finalize payroll.
Learn more about Paycor’s payroll solution:
Legal risks
If you don’t check or fix any payroll errors, you expose yourself and your business to the consequences of these compliance issues whenever you process payroll. You may face an audit, penalty, or lawsuit for incorrect employee wages.
If any of these situations arise, the legal fees and penalties will typically far outweigh any money you would have spent on payroll software. In fact, many come with compliance monitoring or in-app HR support.
Gusto, for example, will investigate and pay for any tax problems resulting from its error. Meanwhile, Rippling’s Compliance 360 monitors your pay practices to ensure you comply with federal, state, local, and global laws, like mandated sick leave.
Alternatives to doing payroll yourself
There are several different options that you can pursue if you no longer want to calculate your small business payroll on your own:
Manual payroll processing FAQs
DIY payroll saves money, but not time
Manual payroll might be your small business’s only option as you scour for investors, drum up funding, and funnel what little you have straight into your business operations. Completing payroll yourself may be your reality until your headcount and profit margin grow enough to warrant payroll software or services.
Until then, take advantage of our payroll resources below to better understand the process and perhaps make it just a little less tedious.
- Best Free Payroll Software
- Methods of Conducting Payroll: In-House vs Outsourcing
- How Long Does Payroll Processing Take?
- What is the Best Payroll Schedule for Your Business?
- What Are the Best Methods for Paying Employees?
- How to Avoid These 3 Costly Payroll Mistakes
- Employee Classification: HR’s Guide to Classification Compliance.
- How Much Does HR Software Cost?
- How to Create the Perfect PTO Policy