Key takeaways
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a modern telephony technology that uses the same resources as computers to communicate using Information Technology (IT) equipment. Modern telephony technology allows users to communicate audibly using VoIP devices or computer resources.
What is VoIP?
Voice over Internet Protocol is a technology that allows users to make voice calls by converting voice into a digital signal and sending it over the internet in data packets using IT equipment. Voice over Internet Protocol uses packet switching that is different from circuit switching used by traditional telephones in homes and business offices. VoIP provides more communication options by supporting audio calls, video calls, voicemail, instant messaging, team chats, email, and text messaging using a VoIP phone or a computer device.
Read more: What is VoIP? A Comprehensive Guide
How reliable is VoIP?
Voice over Internet Protocol phone systems have proven more reliable than traditional or landline phone systems. VoIP phone systems do not rely on physical infrastructure such as telephone wires or a telecommunications facility that connects subscribers’ phones and transfers calls between subscribers. The traditional phone system’s physical infrastructure is more exposed to natural disasters, energy surges, traffic congestion, and wear and tear, making landline systems more vulnerable than VoIP systems.
Redundancy contributes significantly to ensuring VoIP providers are functional by implementing redundant data centers that can reroute calls during any potential outage. Disaster recovery systems can forward calls to employee devices during an ongoing outage or emergency. Unlike traditional phone systems, VoIP doesn’t rely on physical infrastructure exposed to natural disasters like hurricanes or tornadoes.
Flexibility is another feature of VoIP systems that makes them reliable. Employees with an internet connection can connect anywhere globally and communicate. Finally, VoIP systems are less susceptible to network and hardware outages due to best practices like monitoring frequently, network redundancy, regular network updates, and having a backup plan.
Common VoIP problems
VoIP systems are far better than traditional phone systems due to VoIP’s reliability, cost savings, and the flexibility to make calls from anywhere with an internet connection. At times, businesses will have to troubleshoot VoIP problems, and here are some common issues to address and how to fix them.
Jitter and latency
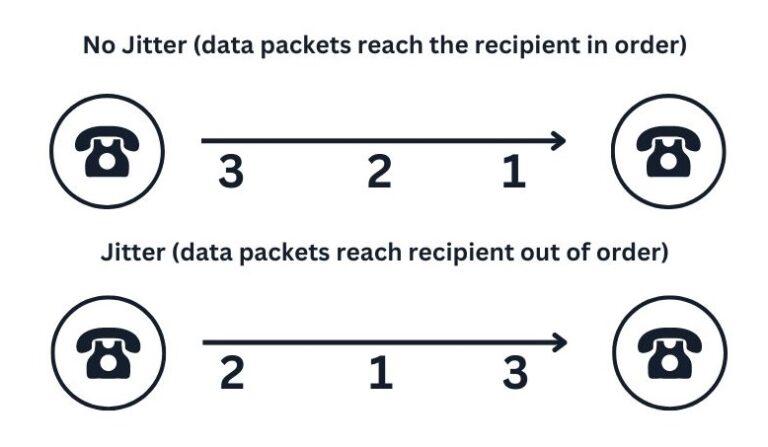
Jitter results from data packets of an active phone call being sent out or ordered to a recipient, making the conversation hard to understand. See Figure 1. Latency occurs when there is an audio delay, and the speaker’s voice takes a long time to reach the recipient. See Figure 2. To avoid jitter or latency, run a VoIP speed test. Removing these two issues requires jitter below 30 milliseconds (ms) and latency below 150 ms.

Businesses can avoid these problems by purchasing a new router that supports faster data speeds or reducing local network traffic by limiting the number of concurrent users. You can also ask your Internet Service Provider to upgrade your internet connection. Installing a jitter buffer may cause a slight delay, but the delay is because the buffer may be reordering the data packets in real time.
Broken or choppy audio
Broken or choppy occurs when the VoIP call is not fully connected, which means certain words are dropped, and voices are cut in and out during the call. You can use the VoIP speed test to confirm that the jitter is below 30 ms. If the jitter is higher than 30 ms, it indicates insufficient bandwidth.
Reducing the number of users or segmenting the network by removing unnecessary traffic from a specific network segment can reduce the jitter. Data-intensive activities like streaming, gaming, or video conferencing can be moved to another network segment to minimize jitter. Adjusting your Quality of Service (QoS) settings will enable you to prioritize specific devices or data types to access the bandwidth for VoIP services over other devices and data types. VoIP phones can use a wireless network to communicate, but if the Wi-Fi is intermittent, consider switching to an Ethernet cable connection to the internet.
Phone echoing
Echoing occurs when one or more voices are loudly repeated during the call, interrupting other recipients from hearing the conversation.
The common causes of echoing are:
- A recipient has a speakerphone on
- Electromagnetic interference
- Damaged equipment
- Slow internet
To combat echoing, users must turn off speakerphones. If a user is using a headset, the headset will need to be tested by making a call with a headset not used on the call or a call without a headset. If the headset continues making noises on a different call, the headset must be replaced.
An internet connection or bandwidth issue can be the cause of the echoing. Businesses can check the internet speeds using an internet speed test. If your speed test is insufficient for VoIP traffic, you can contact your internet service provider to explore options for increasing speeds. Electronic magnetic interference occurs when electronic devices are too close together.
No sound after the call connects
When a connection is established and no sound is heard, the most likely cause is data packets going to the wrong IP address or the firewall is blocking inbound data packets. A system administrator may also need to check that the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Application Layer Gateway (ALG) is turned off. The SIP ALG inspects VoIP traffic to prevent problems with firewalls, and it’s often turned on as a default setting on routers and broadband hubs. Real-time Protocol (RTP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets are required for VoIP services.
Also, all recipients’ VoIP extension’s Codec settings should be checked to ensure they use the VoIP codec (G.711, G.722, Opus) that compresses and transmits all audio data during a call.
Phone doesn’t ring on inbound calls
A VoIP phone not ringing when you’re expecting a call from a potential client can lead to losing a potential client. The first item to check is ensuring your VoIP phone is not set to Do Not Disturb and checking your call forwarding setting to ensure the expected call was not redirected. Make sure your VoIP phone is registered with your current VoIP service provider and that the phone is logged into your VoIP application.
Additionally, check for damaged cable connections and ensure the cables are securely connected to the correct devices. Ensure the router is in an open area and not blocked by a door or wall that can hinder the Wi-Fi connectivity. Lastly, check your router to ensure it’s functioning correctly and has enough bandwidth to handle the expected call volume concurrently. Adjust your router’s Quality of Service feature to prioritize specific devices and the associated bandwidth.
Dropped calls
The most likely cause of dropped calls is insufficient bandwidth. Another possible cause of dropped calls is the software may be incompatible with the VoIP hardware and equipment. A software update may be required to ensure compatibility between the software and hardware. Check with your VoIP service provider to ensure your VoIP system has the latest software updates.
If the problem is still unresolved, disconnect all devices connected to the VoIP network and reconnect one device at a time to see if you can isolate and replace the bad device. Check your UDP timeout and Router timeout settings to verify that they are not causing the dropped calls, and call your VoIP service provider to assist in checking the timeout settings.
One VoIP phone works while another one doesn’t
If one VoIP phone works and another doesn’t, the VoIP phone that doesn’t work may not have its MAC address registered or not correctly configured and needs updating. Make sure the MAC address is registered and the configuration is updated. Take the non-functioning VoIP phone to a working office space with a working network port and test the phone again. Contact your VoIP service provider for firmware or configuration updates if applied updates do not work. If neither update works, the VoIP phone will need to be replaced.
Best practices to implement to avoid VoIP problems
A robust and reliable VoIP phone system starts with implementing the known best practices. A reliable VoIP system begins with selecting a good VoIP service provider who follows the best practices consistently. A vital element of a good VoIP phone system starts with network stability.
Network stability
- Bandwidth requirements: must be adequate to handle VoIP calls with minimal packet loss; therefore, bandwidth must be between 5-25Mbps.
- QoS configuration: This helps prioritize VoIP traffic on routers by adjusting the QoS setting.
- Router selection: Select a router specifically designed for VoIP traffic.
Selecting a hosted VoIP service provider
- Reliability: Select a VoIP provider with a history of high uptime and reliable service.
- Customer Support: Choose a VoIP provider with good 24/7 customer support and available technicians who can troubleshoot.
Read more: What is Hosted VoIP? A Complete Guide
Device management
- Software updates: Updates are applied to VoIP software and firmware that addresses security vulnerabilities and bugs, as necessary.
- Hardware checks: routinely schedule checks for loose cables and damaged connections.
- Device configuration: Verifies VoIP phones are correctly configured.
Security practices
- Strong passwords: The use of complex passwords is mandatory.
- Two-factor authentication: Enabling two-factor authentication is required.
- Encryption: Confirm your VoIP service provider implements end-to-end encryption for secure communication.
Read more: VoIP Security Guide: Tips, Risks & Security
Troubleshooting practices
Run a speed test: Perform a regularly scheduled speed test to address any latency or other potential concerns.
Disable SIP ALG: Turn off this setting to prevent any interference with VoIP traffic.
Check network settings: Review network settings to verify proper routing and firewall configuration settings.
Strategies for Troubleshooting VoIP Problems
Using established best practices can help minimize VoIP problems so that troubleshooting is a rare occurrence. Typically, some components in a VoIP phone system will require troubleshooting steps to identify the problem.
- Checking your network configuration: Ensure your firewall, routers, and switches are configured to support VoIP traffic.
- Internet and VoIP speed test: Running speed tests to check for latency or bandwidth issues as required is a necessary test when performance is noticeably slower or inconsistent.
- Configure QoS: Ensure VoIP traffic is prioritized over other data types on routers and switches.
- Update firmware and software: Phones, routers, and all associated VoIP devices must have the latest version, as required.
- Change the UDP timeout duration: Increase the timeout to at least 60 seconds, allowing for longer calls.
- Disable SIP ALG: Disable the SIP ALG setting to eliminate the effect on VoIP data streams, which is enabled on commercial routers.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN separates your VoIP traffic from all other types of traffic, minimizing internet congestion on the VPN.





